Let us explore what is design thinking and who practices it? Before we head on to the read, let me ask you some questions!
Did you ever think about why a mobile phone needs a wireless charger? Why there is a home for the aged or homeless? Why do we need a venture capitalist as a financier?
Design Thinking and Design thinkers:
Let us explore a few insights on the concept of Design Thinking, which is gaining a lot of attention in various fields especially in the world of leadership, business and entrepreneurship.
Design thinking is a kind of empathetic skill that the thinker exercises to find a solution for human problems in the world of entrepreneurship. IN the process of finding solutions, Design Thinking challenges the established assumptions of an idea/product/problem and provides a new definition to those problems in the process of finding alternative solutions.
Let us take the example of Smart parking sensors, wireless chargers, car parking lifts, these are all the outcomes of a problem for which the reasons are complex and yet times multi-dimensional. So the approach needs to be not just scientific but also user/people-centric.
Origin and history of design thinking:
Design thinking is an offshoot of research acumen mindset. The inquisitive mind of a researcher or a problem solver explores the solutions by exploring theory and practice. It is a continuous effort of a researcher in numerous disciplines such as arts, science, business, medical science, engineering and technology, etc to address real life problems to provide solutions. In this journey, the thinkers/researchers/innovative minds started identifying the root cause through a more structured format from the perspective of human needs, technological needs, and strategic innovation needs and emerged into a new way of thinking process called “Design Thinking”. So to say, Design Thinking is a solution-based approach to solving business/consumer problems which are coined as Wicked Problems by Horst Rittel, a Design Theorist, in mid-1960s. Wicked problems are by design they are very complex and multi-dimensional and require a collaborative approach and involve a deep understanding of humans.
One of the wicked problems of current times is the issue of Global Warming and Climate Change. This is one step ahead of scientific research approach. According to Bryan Lawson, professor at the School of Architecture of the University of Sheffield, UK, scientists are problem-focused problem solvers and designers are solution-focused problem solvers. Nigel Cross (1982) in his work Designerly ways of knowing, mentioned that solution focused problem solvers are “designerly” way of problem solvers. This thinking process relies on generating fairly quickly a satisfactory solution, rather than on any prolonged analysis of the problem.
In 1987, in his book Design Thinking, Peter Rowe, Director of Urban Design Programmes at Harvard, focused on the inquiry way of design approach to design the urban constructions and buildings. Further, it gained more prominence with the works of Tim Brown of IDEO from 1990 to date.
The process of Design Thinking:
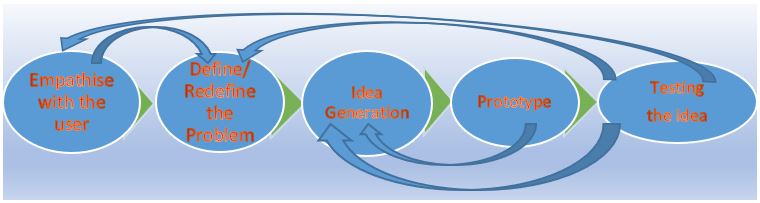
Design thinking is a process and in every stage, it has a chance to improve the idea further and better through critical thinking and learning from the outcomes from each stage. These stages are majorly five, starting from empathy, define, ideate, prototype, and test. It is a continuous process and reviews the results of every stage and improves the idea further and then tests in the market. So it is an iterative and nonlinear process. This process challenges the scientific method of problem-solving approach, which is assumed to be a linear process.
Design thinking is an out of box thinking and in the era of artificial intelligence and robotics, still it is human in nature. The reason is, it emphasizes the Empathic Understanding of the problem. It means, understanding of a problem from the user/people’s point of view and tries to deal with the non-measurable influencing factors like needs, motivators, emotions and behavioral aspects. Most of the socially innovative and creative ideas like equal paid paternity, 3D-printed homes and neighborhoods, personalized tuition centers, artificial light to encourage food growth etc are the outcomes of this problem-solving approach through design thinking.
Tim Brown, CEP-IDEO, in his book Change by Design mentioned that, “Design Thinking process is strongly dependent on creating a holistic and empathic understanding of the problems that people/users face. He summarized in his book that, Design Thinking is a third way of approach to a problem, i.e., it is a problem-solving approach in the area of design and combines holistic people/user-centric perspective with analytical research in an integrated way aims to create innovative functional solutions.
Will Design Thinking approach solve the problems of everybody?
The brief history narrated above about Design Thinking demonstrates the increased scope and progression of Design Thinking in various disciplines and numerous fields’ practitioners are applying Design Thinking as a problem solving approach.
- Developers and builders
- Education
- Business
- Food innovation
- Design Research
- Equity Designers who work on equitable communities
- Transition designers, who encourages societal transition towards more sustainable future
Role of Education system in fostering Design Thinking
Educational institutions, especially higher educational institutions (HEIs) contribute to the research and community development through its progressive and inclusive curriculum and resources. HEIs with the entrepreneurship education can take up academic initiatives such as incubation centers, accelerator Programmes, value based education, innovation labs, and design labs in various disciplines to infuse Design Thinking mindset in students. Examples of Design thinking from real world of business/enterprises showcases how businesses can achieve success with creative leadership. Education system with a participative and inclusive pedagogy can foster entrepreneurial mindset and creative leadership skills among students.
To sum up, Design Thinking is an approach to connect unconnected dots.
Now, I leave all the readers with few questions to explore:
Dot 1 – Mobile phone (Manufacturer and user), disposes to acquire new one/introduce a new one.
Dot 2 – Users want – two network connections – national and international networks
Dot 3 – Internet connectivity
Dot 4 – Banking transaction
Dot 5 – Purchase groceries during lockdowns
- What is your solution, how do you connect these unconnected dots?
- From the Design Thinking flowchart given below, Is Design Thinking Process linear or non-linear?
- Is the process Simple or Complex?
- Why iterations taking even from a test stage?
Design Thinking Process Flow Chart
References:
Bill Moggridge (2010) Design Thinking: Dear Don
http://www.core77.com/posts/17042/design-thinking-dear-don-17042
Don Norman (2013) Rethinking Design Thinking
http://www.core77.com/posts/24579/rethinking-design-thinking-24579
Rikke Friis Dam and Teo Yu Siang Design Thinking: Get a Quick Overview of the History
|https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/design-thinking-get-a-quick-overview-of-the-history
Tim Brown, Change by Design: How Design Thinking Transforms Organizations and Inspires Innovation Introduction, 2009, IDEO
Dr. Sudha Mavuri is an Associate Professor in the Department of Economics, and the current Dean of Arts, Management and Social Science, Skyline University, Nigeria. She has a Ph.D in Economics from Osmania University, Hyderabad, India.
You can join the conversation on Facebook @SkylineUniversityNG and on Twitter @SkylineUNigeria
